Machine Vision
9 May, 2019

Looking Through the Lens of Automation
I remember my first interaction with machine vision. It was exciting, because I had this image of all the things you’ve seen in the movies. I always remember the scenes in “Terminator” where you were looking through the eyes of the machine, and seeing what it saw. Little did I realize that while that was possible, it was not something easily accomplished.
Machine vision is an exciting tool in automation; it takes machine sensing to the next level. Where before the machine knew if something was there or not, hot or cold, metal or plastic, now the machine knows what is there, what shape it is, what color, position, orientation, so many more parameters than just the simple sensing from before. There’s a huge upside to using machine vision, but there is one immense challenge. All of this data that machine vision gives you is just that, data. It’s not useful until someone makes it useful, and that can be a daunting challenge.

I was on a team trying to detect defects in roofing products (shingles) with machine vision. Everyone was working on various tasks, and having various levels of success. Challenges abounded. Limitations of vision systems were quickly realized. Tools were needed, and used, to overcome those challenges but at the cost of processing speed. The best example I have of these challenges was trying to find black holes on black shingles. To a human, it’s easy. We have the largest processing power of any one component in a factory, and our brains are wired for visual input and image processing. For a vision system, it doesn’t work that way. Lighting and contrast matter greatly, and a small change in conditions can create a huge change in performance. One of our team was having difficulty programming for these holes, and he asked me to help. Over four hours we both tried our best, and when we got back together, we compared. He was still having trouble, I was hitting over 90% of the holes (not good enough, but much better than before.) His comment was “Well, that’s a white shingle. Those are easy.” I showed him the raw image of the unit we were looking at, a black shingle. I had to adjust so many parameters to get the holes to show that the shingle was white after the image processing. Challenges, overcome with tools. This might give you an idea of why vision is so tricky.
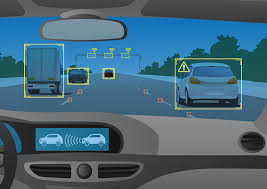
The news is full today with machine vision, because we’re seeing it on our roads. Self-driving cars utilize machine vision among other sensors for control functions, including the all-important collision avoidance. Machine vision is a very black and white function, though. There’s no intuition or anticipation like a human has. Either parameters are good, or they’re not. Machine vision can detect the quick glances of a driver about to merge into your lane, but has to be told that those glances mean you need to get out of the way. Machine vision can pick up things that humans will not because they can look at everything at once, but that advantage is diminished greatly by the limitations on programming for responses.
Where does this lead us to for the future? With the amazing amount of data machine vision can deliver, the processing power of today’s modern computers, and the advances in machine learning and AI, the future’s so bright you’re going to need shades. Self driving cars will be the catalyst for huge advances in utilizing vision and AI in conjunction to create a truly smart machine. The black and white world of machine visions will slowly become grayer, and decisions will become more human-like. The Einsteins of the future are going to be the ones who figure this out, how to make human decisions with machines. The day that happens, we’ll see a quantum leap in machine usage, because at that point we’ve made not just a tool to use for tasks, but a potential partner to help us with living.
Right now, the limitation is becoming the programmer, the human. As we dive deeper into how we learn, what intuition is, and how to recreate that in a logical format we will see amazing things come from machine vision coupled to AI. Self-driving cars are just the first steps. Imagine a world where machines can see like humans, use that vision to make decisions, and take action on those decisions. Automated health care, automated personal services, and so much more are in the future. Will we see the Jetsons, or Terminator in our future? That again is up to the programmers. I’m hoping for the Jetsons.
Credit: Steve Nordin-The Wake Industrial Team












